 Spring事务测试分析
Spring事务测试分析
# Spring 事务测试分析
# 1. 前期准备
⭐ pom 依赖:Spring 核心、mysql、jdbc、数据库连接池
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring-jdbc 用于配置JdbcTemplate -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid 数据库连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.8</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
⭐ application.xml:bean 配置、配置 mysql、事务
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<bean class="com.zqc.service.MyService" id="myService">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>
<property name="myService" ref="myService"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置mysql -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="xxx"/>
<property name="username" value="账号"/>
<property name="password" value="密码"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置jdbc-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" p:dataSource-ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- 配置事务-->
<bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"/>
</beans>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
⭐ MyService :使用 jdbc 操作数据库,后面将对改代码进行修改并测试
public class MyService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void login() {
System.out.println("登录!");
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')");
test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NEVER)
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')");
}
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return jdbcTemplate;
}
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 2. 事务失效说明
# 2.1 事物失效的原因
- 方法不是 public 的,@Transactional 只能用于 public 方法上,否则事务不会生效,如果要用在非 public 方法上,可以开启 AspectJ 代理模式
- 数据库不支持事务
- 没有被 Spring 管理
- 异常被吃掉,事务不会回滚(或者抛出的异常没有被定义,默认为 RuntimeException)
- 方法互相调用时注解失效,需要分析是普通方法还是代理方法的调用,只要代理对象调用其他方法时注解才会生效。
# 2.2 方法内调用事务失效说明
下面详细说明第 5 点:方法互相调用时注解失效
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')");
test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NEVER)
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
第一部分已经列出的代码,test1() 和 test2() 分别插入数据到数据库,其中 test1() 调用 test2(),那么此时会出现什么问题?
事务传播机制:
- propagation_required:如果外部没有事务,就开启一个事务;如果外部存在一个事务,就加入到该事务中。
- propagation_never:如果外部事务不存在,则不使用事务;如果外部存在一个事务,则抛出异常。
错误理解:因为 test2() 的事务传播机制为 never,所以 test1() 调用 test2()时, test2() 会抛出异常。
正确理解:此时事务失效,两条插入语句正常执行。
🚩 那么,事务为什么会失效呢?
创建 Spring 容器并启动,从容器中获取 MyService 这个 Bean 对象。
public class SpringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
MyService myService = context.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.test1();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
通过 Debug 进行观察,可以看到:
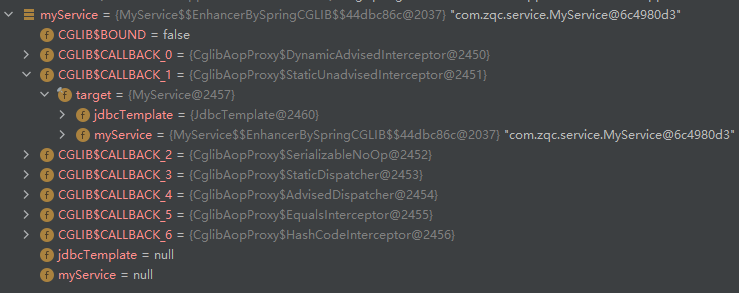
可以看出 myService 是通过 SpringCGLIB 进行增强的代理类,后面称为 MyService$$EnchanceByCGLIB。其中包含很多属性,介绍一下我明白的:
- CGLIB$CALLBACK_1
- target:被代理对象,后面称为 MyService$$Original
- jdbcTemplate:MyService 中注入的 Bean 对象
- myService:增强后的代理对象,也就是 MyService$$EnchanceByCGLIB
- target:被代理对象,后面称为 MyService$$Original
- jdbcTemplate:为 null,这个就是在 MyService 中注入的 Bean 对象,但是它为代理对象,所以为 null。
下面再接着说为什么会失效呢?
当我们调用 test1() 的时候,实际上调用的是 MyService$$EnchanceByCGLIB 的 test1() 方法,可以保证 test1() 的事务不会失效;但是,在 test1() 方法内调用 test2() 时,实际上调用的是 MyService$$Original 的 test2(),也就是 MyService$$EnchanceByCGLIB.target.test2(),也就是普通的 test2(),所以它的事务不会生效。
🚩 解决方案
将两个方法放到两个类中,在其中一个类中注入另一个类后再调用。
自己注入自己
public class MyService { ... private MyService myService; // 自己注入自己 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public void test1() { jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')"); myService.test2(); // 调用注入的 myService 的 test2() 方法 } @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED) public void test2() { jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')"); } ... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 3. 事务传播说明
# 3.1 事务传播机制
- REQUIRED:如果外部没有事务,就开启一个事务;如果外部存在一个事务,就加入到该事务中。适用于增删改。(常用)
- SUPPORTS:如果外部事务不存在,则不使用事务;如果外部存在一个事务,就加入到该事务中。适用于查询方法。(常用)
- MANDATORY:如果外部事务不存在,抛出异常;如果外部存在一个事务,就加入到该事务中。
- REQUIRES_NEW:如果外部没有事务,就开启一个事务;如果外部存在一个事务,挂起外部事物,创建新的事物。
- NOT_SUPPORTED:如果外部没有事务,不开启事务;如果外部存在一个事务,挂起外部事物。
- NEVER:如果外部事务不存在,则不使用事务;如果外部存在一个事务,则抛出异常。
- NESTED:嵌套事务,如果当前事务存在,则嵌套在事务中执行。如果当前事务不存在,则创建一个新事物。如果嵌套事务发送回滚,只回滚嵌套部分的事务。
# 3.2 事务传播机制测试
在外部事务使用 propagation_required 的前提下,通过修改抛出异常位置和内部事务的传播机制,测试以下九种情况。
| 里面异常,外面不捕获 | 里面异常,外面捕获 | 外面异常 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 都回滚 | 都回滚 | 都回滚 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 都回滚 | 外面不回滚,里面回滚 | 外面回滚,里面不回滚 |
| NESTED | 都回滚 | 外面不回滚,里面回滚 | 都回滚 |
REQUIRED:两个独立的事物
NESTED:里面的事物嵌套在外面
测试方法
外面异常,全部回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')");
myService.test2();
throw new RuntimeException("xxx");
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
里面异常,全部回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')");
myService.test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')");
throw new RuntimeException("xxx");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
里面异常,外面捕获,全部回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x1', 'xxx1', '10')");
try {
myService.test2();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
myService.test2();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into course (c_id, c_name, t_id) value ('x2', 'xxx2', '20')");
throw new RuntimeException("xxx");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
用相同的方式测试其他的传播机制。
